Image source: bcairquality.ca
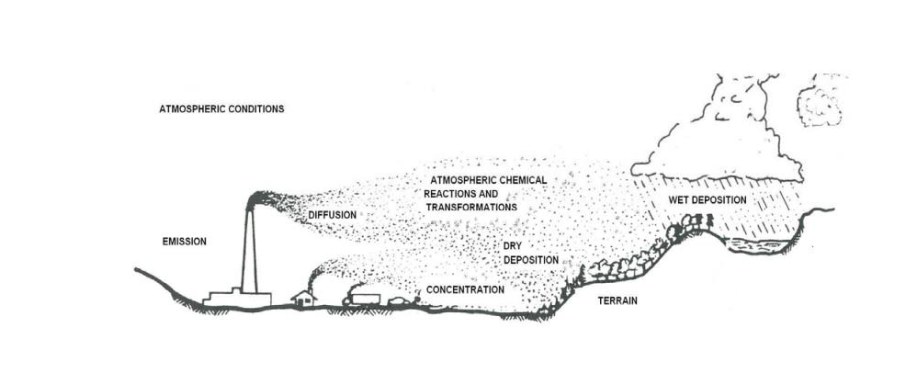
Air dispersion modelling is today's key concept in environmental regulation. Dispersion modelling utilizes information about sources, meteorological conditions and topography to compute the behavior of pollutants in the air.
Protecting and Managing the Ambient Air Quality
In the past,
air pollutant concentrations resulting from emission sources were estimated manually. However, in today’s advancing world, dispersion modelling is facilitated with powerful software, which can perform thousands of calculations in no time.
Air dispersion models are used for scrutinizing scenarios that would otherwise be extremely expensive, challenging or destructive to do in the real world. For instance, dispersion models can be used to answer tough questions such as:
- Which emission sources are responsible for air pollution?
- Should a proposed factory be built or not?
Not only can a model identify the contributors to poor air quality, but it can decide whether a proposed new source is a threat. Thus,
air dispersion models help in decision making so as to protect and manage the ambient air quality.
When a company plans to construct or modify an industrial facility, an air dispersion model plays a major role in the
air permitting process.

Air quality is of growing concern in communities across B C because it can affect our health and the environment. It is often assumed that air quality is determined by how much is emitted into the air;
Approved Air Dispersion Models
·
AERMOD
·
CALPUFF
·
Regional Scale Models
·
AERSCREEN
·
Puff Models
Get to know in detail about the
applications of air dispersion models in British Columbia.
Dispersion Model Results– How Accurate or Inaccurate?
Dispersion models are based on our understanding of how pollutants move through the atmosphere and what the pollution concentration is at particular points.
Used to calculate the downwind air concentration of air pollutants emitted from industrial plants, vehicular traffic or accidental chemical releases, all dispersion models are a representation of reality.
At the end of the day, these are all models, which is why we cannot expect them to provide perfect results at all times.
This is because our understanding of the details of the behavior of air pollution is incomplete, and so the equations which describe this process are incomplete too. Air dispersion models need inputs (emissions, weather and geography). Poor quality inputs give way to poor quality output. The dispersion model is powerful yet not so powerful that it can correct poor input magically.
It’s crucial to select the correct model for a given situation and ensure all the inputs have been checked for totality and accuracy. Modellers must be skilled enough to guide decision-makers in the correct use of output.
The
Ministry of Environment archives
air quality data to check how accurate a model performs by comparing model predictions to actual observations. This offers some level of confidence in the model and helps in determining any parts of the model that need improvement.
British Columbia’s Environmental Consultants
Do you need assistance for
air permit application?
A.Lanfranco and Associates can help.